- Home
- About WVN
-
WVN Issues
- Vol. 1 No. 1 (Oct. 2017) >
- Vol. 2 No. 1 (Feb. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 2 (Jun. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 3 (Oct. 2018) >
- Vol. 3 No. 1 (Feb. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 2 (Jun. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 3 (Oct. 2019) >
- Vol. 4 No. 1 (Feb. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 2 (Jun. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 3 (Oct. 2020) >
- Vol. 5 No. 1 (Feb. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 2 (Jun. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 3 (Oct. 2021) >
- Vol. 6 No. 1 (Feb. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 2 (Jun. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 3 (Oct. 2022) >
- Vol. 7 No. 1 (Feb. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 2 (Jun. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 3 (Oct. 2023) >
- Vol. 8 No. 1 (Feb. 2024) >
-
Events
- CIES 2023, Feb. 14-22, Washington D.C., USA
- ICES 4th National Conference, Tel Aviv University, Israel, 20 June 2021
- 2022 Virtual Conference of CESHK, 18-19 March 2022
- ISCEST Nigeria 7th Annual International Conference, 30 Nov.-3 Dec. 2020
- 3rd WCCES Symposium (Virtually through Zoom) 25-27 Nov. 2020
- CESA 12th Biennial Conference, Kathmandu, Nepal, 26-28 Sept. 2020
- CESI 10th International Conference, New Delhi, India, 9-11 Dec. 2019
- SOMEC Forum, Mexico City, 13 Nov. 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Geneva, 14-15 Jan. 2019
- 54th EC Meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 14 Jan. 2019
- XVII World Congress of Comparative Education Societies, Cancún, Mexico, 20-24 May 2019
- ISCEST Nigeria 5th Annual Conference, 3-6 Dec. 2018
- CESI 9th International Conference, Vadodara, India, 14-16 Dec. 2018
- ICES 3rd National Conference, Ben-Gurion University, Israel, 17 Jan. 2019
- WCCES Retreat & EC Meeting, Johannesburg, 20-21 June 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Johannesburg, 21-22 June 2018
- 5th IOCES International Conference, 21-22 June 2018
- International Research Symposium, Sonepat, India, 11-12 Dec. 2017
- WCCES Info Session & Launch of Online Course on Practicing Nonviolence at CIES, 29 March 2018
- WCCES Leadership Meeting at CIES, 28 March 2018
- 52nd EC Meeting of WCCES, France, 10-11 Oct. 2017
- UIA Round Table Asia Pacific, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 21-22 Sept. 2017
- Online Courses
|
Abstract Effective teachers need to be both knowledgeable as well as empathetic. The main objective of this was to examine how the secondary teachers apply empathetic responding in teaching learning process. Two research questions were examined; How is the teachers’ existing knowledge on empathetic responding; How teachers apply it in teaching learning process. Goalman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory and the Person - centered theory of Carl Rogers were studied to create a self -made questionnaire and the checklist to observe the lessons and the focused group interview. Teddie and Tashakkori (2009, P. 151) ‘s parallel mixed method design was used for the first phase of this research. Questionnaire for purposively selected Sample of 130 teachers were administered while the 10 lessons were observed and gathered data were analyzed using descriptive statistics such as frequencies, percentages, mean scores The result indicated that the existing knowledge about empathetic responding are satisfactory. But 72% of teachers said that they do not have an understanding, how to respond empathetically, in teaching learning process and advantages of it. 8 teachers out of 10, did not concern about empathetic responding while observing lessons. For the second phase, an action research was conducted for the selected five teachers. Data gathered from Observation checklist, focused group interview and reflective journals while and after intervention, were analyzed from thematic analyzing method. Results indicated that each selected teacher uses empathetic responding in teaching learning process with certain differences and difficulties. Through the second cycle of intervention, all were able to apply the skill with satisfactory level to them. They believe that it is a good way to build better relationship with students. Researcher suggest in teacher education programme, empathetic responding skill should be practiced more as it is the core in communication. Key words - Empathetic responding. Mixed method , secondary teachers Background of the problem Empathy is an important variable in influencing the quality and effectiveness of a helping relationship. The concept of empathy has been described in many ways by researchers. According to some, it is the basic cognitive function or ability of being aware of others’ thoughts and feelings (Bartnett, 1990; Borke, 1971, as cited in Şahin, 2012). Empathy refers to being able to respond to emotions, sharing the feelings of individuals, and reflecting them as if in a mirror. It also helps to establish good relationships with people, to understand them, and share their feelings (Krznaric, 2008). Empathy plays an important role in guidance and counselling process. It is the main source of the counselor – client relationship. It is described by Carl Rogers, father of counselling. Positive relationship makes difference in any ones’ life .Teacher- pupil relationship affects positively to students in their throughout their life. Empathetic responding is the main source in building a healthy relationship as well as an effective teaching learning environment. (Pigford: 2001). Teachers’ lack of attention, care and empathic responding affect for the students’ negative behaviors. Such behaviours are, truancy, isolation, insulting and disturbing others, dictions, feeling with negative self - concept, poor academic performance etc. (The American academy of child and adolescent psychiatry, 2004) Teacher is the closest person who identifies the needs of the students’ very first. The following table shows the summary of the problems which were affected by senior secondary students. Day by day, socio emotional and behavioral problems of students increase. Some problems are created by teachers due to the lack of empathic responding and teacher qualities in all over the world. Some problems affected to socio emotional wellbeing of students are teacher’s ridicule ,teacher’s unfair treatments ,teacher’s insulting in front of others ,Lack of respect for students ,Blame harshly. OECD report (2018). Fleming, Mackrain and Lebuffe (2013) studied about teacher – pupil relationship. They mentioned that many studies and clinical reports have shown that there is an improvement of developmental disorder in children due to the distance with the teacher. In sri Lankan survey, in 2016, mentioned that 30.5% of students between age 5- 17 do not attend school due to negative effect of teachers. Kakgodaarachchi (2017) has revealed so many problems which need the counselling assistance. some problems are love affairs, family related problems and pressure from friends and parents, and biological problems. So, if the teachers are competent enough to communicate properly applying empathic responding, many problems can be minimized. School counselor is unable to deal all the problems of students in a school. The question raised in me. If most of the teachers are professionally qualified with Post Graduate Diploma in Education, or Bachelor of education or National diploma in teaching, why can they apply empathic responding in their communication with students in teaching learning process. The main objective of this was to examine how secondary teachers apply empathetic responding in teaching learning process. The sub objectives are, to find out the teachers’ existing knowledge on empathetic responding, to find out how teachers apply ER in teaching learning process. Literature Review Reviewing literature gives a direction for the research to find the gap between the theory and the practice as well as a critical evaluation of the works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Empathy and Empathetic responding Empathy , empathic responding ,empathic inference , inference , empathic accuracy or accurate empathy are key terms which provide similar meanings. “Empathy as an effective response that stems from the apprehension or comprehension of another’s emotional state or condition and which is similar to what the other person is feeling or would be expected to feel” Eisenberg and Fabes (1991) Considering the definitions of empathy , the general meaning of it is the ability to perceive the other person’s emotions , feelings as well as the cognition and respond properly . ER is described as if walking in another’s shoes , entering into another person’s frame of reference , or having the ability to experience life as the other person does by temporarily entering into the client’s world of thoughts , meanings and feelings. (Mline ,1990). Elements and characteristics of Empathy Empathy is consisted with three major elements. They are; Cognitive component – Perception of others Affective component - Feelings and thoughts Behavior component- verbal and non- verbal communication Characteristics of Empathy; According to Cormier & Hackney (1987 P:38), the primary skills associated with the ER in counselling as follows
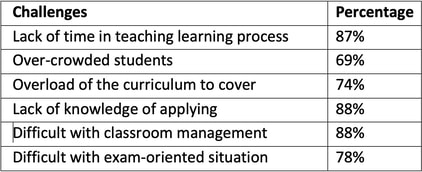
Relationship between empathetic responding and student behaviour Research on empathic responding highlights its importance in teaching learning process. But the extent of the usage of ER may differ from country to country. Cooper (2004) emphasis that empathic teachers tend to be highly moral. Researcher agree with it. If a person can listen carefully and respond showing that he or she is understood by wordings or non-verbal cues, such a teacher is with good qualities. According Anderson and Tettegah (2007) cited in Barr(2010) mentioned that Empathic responding is the ability of teacher to perceive the student’s feelings and thoughts which related to cognitive and affective domain . Young (2016) revealed that teacher–student conflicts may occur due to the perceived lack of teacher. Theoretical Background of the theory Goalman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory and the Person -Centered Theory of Carl Rogers are suitable theories for this study. Carl Rogers as the humanistic psychologist introduced three condition in a counselor –client helping relationship in his Person -Centered approach in 1956. One of the conditions is Empathy. (Cormier & Hackney, 1987). Dr Daniel Golemen (1996) introduced five components in Emotional Intelligence (EI). Empathy is one of the components. Both theorists paid attention on effective human relationships. In the education set up ER is the most important to build better and healthy teaching learning environment interacting each other properly. Research methodology Research design is the core of a result in a study. Gathering data from different methods support for proving the results of the research. Therefore Mixed method research design was the suitable method this research. Mixed method was defined as “Mixed method research is the type of research in which a researcher or team of researchers combines elements of qualitative and quantitative research approaches : use of qualitative and quantitative view points , data collection , analysis, for the broad purposes of breadth and depth of understanding and collaboration” . Johnson et al (2007, p,123) Teddie and Tashakkori (2009, P. 151) ‘s parallel mixed method design was used in the first phase of this research while an action research was conducted in the second phase. “Parallel mixed designs (“Parallel Mixed-Methods-Design”) – In these designs, one has two or more parallel quantitative and qualitative strands, either with some minimal time lapse or simultaneously; the strand results are integrated into meta inferences after separate analysis are conducted; related QUAN and QUAL research questions are answered or aspects of the same mixed research question is addressed (Schoonenboom and Johnson (2017: p217). The survey design was selected for the quantitative method while an action research was used in the second stage. Sample Purposive sampling method was used in the second stage to reach the success of the research. 130 teachers for the sample were selected purposively. Teachers from grade 2 in teacher service, qualified with Post Graduate Diploma Education or Bachelor of Education or National Diploma in Teaching, who attended Teacher performance courses (Modules) in Minuwangoda Educational Zone in Sri Lanka were selected purposively. All the selected teachers have more than five years of experience. The rationale for the selection of this type of sample is that they all have learnt this in the subject of Educational Guidance and counselling. Instruments Self -made questionnaires, interview schedules and observational check lists were used to gather data from the quantitative research stage. In the action research, reflective journal, interviews and observation notes were used to interpret data. Data analysis: Gathered data were analyzed using descriptive statistics such as frequencies, percentages, mean scores. Qualitative data was analyzed from thematic analyzing method. Results and Discussion First part of the questionnaire, the demographic variables of teachers were included. 130 teachers were selected for the survey research design of the first stage of the research Educational Guidance and Counseling for their professional development course. Table 1: Selection of teachers for the sample for the survey In terms of secondary school teachers’ critical understanding on empathy and empathic responding, a majority of them (72%) were with the satisfactory level while 2% of teachers were more satisfactory level. None of the teachers mentioned that they do not have understanding on empathy and empathic responding. It shows that all the teachers have an understanding in different levels. It is a good comment on teacher education. Therefore it is reasonable to conclude that secondary school teachers have the knowledge and understanding on empathetic responding. Considering male teachers, 5% have not answered while the others answered are in correct. Some descriptive type questions were included in the questionnaire to assess the memory on theoretical background of empathy at the second part of the questionnaire. 17% of teachers have not answered while 2% of teachers answered well. They had the better understanding on empathy. Considering the base of those teachers were qualified in psychology as their major in bachelor degree. Though the rest of the teachers’ responses were incorrect. Considering the questions related to application of empathic responding, 87% of teachers including male teachers mentioned that they do not have better understanding on the application. Most of them have written as unable to / do not know to apply empathy in day today teaching learning process”. Focused group interview was conducted for the selected group with 30 teachers including all types of school to thorough the survey results. Interviews were conducted three times including 10 teachers in a group. Researcher used an interview schedule. All the data were analyzed quantitatively according to the themes. # Perception of the validity of Empathic responding All most all the teachers (100%) said that it is important if they can use it properly. Literature review supported for the result. Many studies mentioned that empathy creates a positive impact in education success in students. # Understanding of the empathic 87% of teachers attempted to explain it with quite difficulties and in correct definitions, while 9% explained the differences with examples. 4% of teachers were silent. All were the male teachers. # Problems encountered when applying empathic responding So many barriers and as well as questions were raised. Table 2: Challenges faced by teachers in using empathic responding Throughout the discussions, negative views, ideas and feelings were noticed. They are; “no use of applying and unnecessary attempt.” “teaching is important than empathic responding” etc .
Ten lessons from four types of schools were observed using a checklist. The main purpose of it was to check whether they apply empathic responding in teaching learning process. No any teacher applies empathic responding methodically. But some characteristics related to ER are displayed. By triangulating the above results analyzed from questionnaire, interviews and observation, it is clear that though the teachers have an understanding on empathy and empathic responding, the way of applying is very difficult. In the second stage (Until the findings of the action research, the first person “I” is used as this art belong to an action research) I wanted to conduct an action research in enhancing five teachers’ empathic responding skill in teaching learning process. In this research context, I maintain a reflective journal since the whole research was started. Specially focused group interviews and observing lessons, I noticed some teachers have negative feelings. I named these teachers as ‘A”, “B”, “C”, ” D” and “E” in this research. The following parts were extracted from my research journals. Teacher “A” “D’- ……Why did he laugh sarcastically? I feel sad and angry. ….. Teacher “B”- …..Working with 45 students, what empathy? What is the use of applying? Really, I am irritated. Question is in me. Why even senior teachers do not care about it” Teacher “C” and “E” –… They argue with me highlighting Sympathy is more powerful than empathy” . I feel that why teachers cannot understand this” With the facts gathered from the survey, I feel how can I empower them to use empathic responding”. So I created an intervention plan for the first circle. As the first step, differences of sympathy and empathy was discussed. Characteristics related empathic responding were discussed. In the second step, some practices on empathic responding were done with the teachers. They engaged with it happily. I observed that two teachers were with negative feelings. Not properly engaged. The used such particles as useless activity. According to the observational checklist The three teachers who have quite positive feeling, display the characteristics related ER. The improvement of applying the ER can be identified. # They try to maintain “some non - verbal behaviors like “eye contact” as far as they can. # When students stand up to say something, they start with” yes’ # They attempted to say “You mean, you suppose……” In the second circle of the intervention, I paid more attention on demonstrations. To imitate them, I demonstrate first. A simulation environment was created. Due to this reason, the two teachers’ views started to change little by little. Finally, I conducted a discussion with them. Their wordings are below mentioned. “It is amazing. I used to have distance with students. I feel that now I feel on students due to the training”. “Empathetic responding can create environment of acceptance”. Further he mentioned that “Now I have positive mind on ER” Conclusion of the action research is that through a proper training, teacher capacity on ER can be uplifted eradicating the negative feelings too. Conclusions and suggestions Considering the findings of this study in the first and the second stage, most of the professionally qualified teachers have the understanding on what empathetic responding is .As well as it is evident that though they are qualified, but most of them were unable to apply in teaching learning process. Teachers’ type of schools is not affected in applying empathic responding. It is clear that teacher who is committed to teaching, tend to apply ER. An interesting finding is that training of applying ER, the skill was improved in teachers and positive attitudes were inculcated. Researcher suggests that, empathetic responding skills related professional development activities should be planned and implemented in teacher education programmer. As school - based teacher development programme, workshop with training of ER can be implemented. The effect would be seen as positive teacher – pupil relationship. In school based supervision process, ER skill can be observed. So, one of the evaluation criteria should be ER. Then teachers will tend to apply empathetic responding consciously in their teaching- learning process. References Barr,J.J (2010) .The relationship between teacher’s empathy and perceptions of school culture’; retrieved from www.informatiionworld .com Bozkurt,T. & Ozden ,M.S (2010) The relationship between empathic classroom climate and student’ success, Procedia social and behavioural science 5 (2010) 231-234 Cormier, S & Hackney, H. (1987),. The professional counselor; U.K, Allyn & Bacon Creswell, J.W. (2007). Qualitative inquiry & research design: Choosing among five approaches. (2nd Ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Einsberg, et al (1990). Empathy , conceptualization , Measurement , and Relation to prosocial behavior”; DOI: 10.1007/BF00991640 Milne,A .(2003). Teach your self – counselling ; U.K Holders and Stoughton Schoonenboom, J. and Johnson, R.B. (2017). How to construct a mixed method research”. Open access publication through www. Research gate .net/ publication. Utkur,N. (2019). Determination of Empathy levels of Prospective Classroom Teachers: An Example of the Life Skills Teaching course, Sciendo, Acta Educationis Generalis volume 9, 2019, issue Young (2016). Perceived lack of teacher empathy and remedial classroom conflicts”, Ph D dissertation, Nova Southeastern University
0 Comments
|
AuthorW.L. Preethi Karunathilaka ArchivesCategories Sri Lanka Tea Plantation Image Attribution: Anjadora, CC BY-SA 2.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0>, via Wikimedia Commons |
- Home
- About WVN
-
WVN Issues
- Vol. 1 No. 1 (Oct. 2017) >
- Vol. 2 No. 1 (Feb. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 2 (Jun. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 3 (Oct. 2018) >
- Vol. 3 No. 1 (Feb. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 2 (Jun. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 3 (Oct. 2019) >
- Vol. 4 No. 1 (Feb. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 2 (Jun. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 3 (Oct. 2020) >
- Vol. 5 No. 1 (Feb. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 2 (Jun. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 3 (Oct. 2021) >
- Vol. 6 No. 1 (Feb. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 2 (Jun. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 3 (Oct. 2022) >
- Vol. 7 No. 1 (Feb. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 2 (Jun. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 3 (Oct. 2023) >
- Vol. 8 No. 1 (Feb. 2024) >
-
Events
- CIES 2023, Feb. 14-22, Washington D.C., USA
- ICES 4th National Conference, Tel Aviv University, Israel, 20 June 2021
- 2022 Virtual Conference of CESHK, 18-19 March 2022
- ISCEST Nigeria 7th Annual International Conference, 30 Nov.-3 Dec. 2020
- 3rd WCCES Symposium (Virtually through Zoom) 25-27 Nov. 2020
- CESA 12th Biennial Conference, Kathmandu, Nepal, 26-28 Sept. 2020
- CESI 10th International Conference, New Delhi, India, 9-11 Dec. 2019
- SOMEC Forum, Mexico City, 13 Nov. 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Geneva, 14-15 Jan. 2019
- 54th EC Meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 14 Jan. 2019
- XVII World Congress of Comparative Education Societies, Cancún, Mexico, 20-24 May 2019
- ISCEST Nigeria 5th Annual Conference, 3-6 Dec. 2018
- CESI 9th International Conference, Vadodara, India, 14-16 Dec. 2018
- ICES 3rd National Conference, Ben-Gurion University, Israel, 17 Jan. 2019
- WCCES Retreat & EC Meeting, Johannesburg, 20-21 June 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Johannesburg, 21-22 June 2018
- 5th IOCES International Conference, 21-22 June 2018
- International Research Symposium, Sonepat, India, 11-12 Dec. 2017
- WCCES Info Session & Launch of Online Course on Practicing Nonviolence at CIES, 29 March 2018
- WCCES Leadership Meeting at CIES, 28 March 2018
- 52nd EC Meeting of WCCES, France, 10-11 Oct. 2017
- UIA Round Table Asia Pacific, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 21-22 Sept. 2017
- Online Courses


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
