|
- Home
- About WVN
-
WVN Issues
- Vol. 1 No. 1 (Oct. 2017) >
- Vol. 2 No. 1 (Feb. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 2 (Jun. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 3 (Oct. 2018) >
- Vol. 3 No. 1 (Feb. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 2 (Jun. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 3 (Oct. 2019) >
- Vol. 4 No. 1 (Feb. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 2 (Jun. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 3 (Oct. 2020) >
- Vol. 5 No. 1 (Feb. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 2 (Jun. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 3 (Oct. 2021) >
- Vol. 6 No. 1 (Feb. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 2 (Jun. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 3 (Oct. 2022) >
- Vol. 7 No. 1 (Feb. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 2 (Jun. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 3 (Oct. 2023) >
- Vol. 8 No. 1 (Feb. 2024) >
-
Events
- CIES 2023, Feb. 14-22, Washington D.C., USA
- ICES 4th National Conference, Tel Aviv University, Israel, 20 June 2021
- 2022 Virtual Conference of CESHK, 18-19 March 2022
- ISCEST Nigeria 7th Annual International Conference, 30 Nov.-3 Dec. 2020
- 3rd WCCES Symposium (Virtually through Zoom) 25-27 Nov. 2020
- CESA 12th Biennial Conference, Kathmandu, Nepal, 26-28 Sept. 2020
- CESI 10th International Conference, New Delhi, India, 9-11 Dec. 2019
- SOMEC Forum, Mexico City, 13 Nov. 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Geneva, 14-15 Jan. 2019
- 54th EC Meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 14 Jan. 2019
- XVII World Congress of Comparative Education Societies, Cancún, Mexico, 20-24 May 2019
- ISCEST Nigeria 5th Annual Conference, 3-6 Dec. 2018
- CESI 9th International Conference, Vadodara, India, 14-16 Dec. 2018
- ICES 3rd National Conference, Ben-Gurion University, Israel, 17 Jan. 2019
- WCCES Retreat & EC Meeting, Johannesburg, 20-21 June 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Johannesburg, 21-22 June 2018
- 5th IOCES International Conference, 21-22 June 2018
- International Research Symposium, Sonepat, India, 11-12 Dec. 2017
- WCCES Info Session & Launch of Online Course on Practicing Nonviolence at CIES, 29 March 2018
- WCCES Leadership Meeting at CIES, 28 March 2018
- 52nd EC Meeting of WCCES, France, 10-11 Oct. 2017
- UIA Round Table Asia Pacific, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 21-22 Sept. 2017
- Online Courses
|
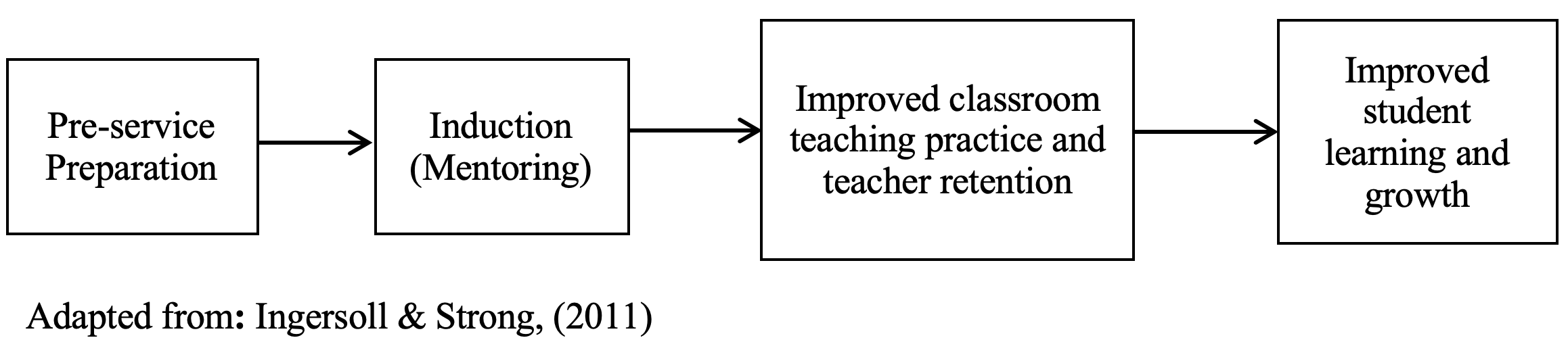
Abstract The objectives of this paper are to study of the use of instructional practices of lower secondary school teachers in Finland and to study the impact of teachers’ professional development on the use of instructional practices. In this research, the TALIS 2013 Teacher Questionnaire data set (BTGFINT2) was used. To answer the research questions, the descriptive statistics and inferential statistics (t test) were used. The first portion of findings showed the use of instructional practices of teachers by using percentage in each item. The second portion showed the impact of teachers’ professional development on the use of instructional practices in the classroom. According to the t test results, we can conclude that the teachers who completed teacher professional development can implement more effectively than those who didn’t complete the teacher professional development such as teacher training, teacher induction program and mentoring program. Therefore, teachers’ professional development is the very important factor for improving teacher’ classroom practices. Keywords: teacher’s professional development, instructional practice. Introduction Modern society demands high quality teaching and learning from teachers. Teachers have to possess a great deal of knowledge and skills with regard to both teaching and assessment practices in order to meet those demands and standards of quality education. The core 21st century skills consist of problem solving and critical thinking, creativity and innovation, and collaboration and communication. These skills are clearly interrelated in a variety of ways, and the development of problem solving skills especially is often tackled through active learning approaches. There are a variety of such pedagogical approaches, including group work and brainstorming, collaborative and co-operative work, and team-based problem solving; these educational strategies are often driven by an emphasis on providing students with the skills and attributes to become self-directed and highly autonomous life-long learners. In order to develop these core 21st century skills in students, the teachers should apply effective teaching learning strategies which can develop these skills at the classroom. In order to use these instructional strategies in the classroom effectively and efficiently, the teacher should complete the professional training and continuous professional training such as the teacher training and induction program. And also, it was found that the teachers with effective training and sound pedagogical background were more successful in their teaching profession. Therefore, professional training process and professional development process is one of the important factors in the teachers’ use of classroom practices. If the teachers have sound professional background and professional knowledge, they can effectively use the various instructional practices in the classroom. In many research, it can be found that there was the relationship between the teachers’ pedagogical practice and their professional development. This paper will prove the impact of professional development on the use of teachers’ instructional practices in the classroom with the quantitative evident. This paper aims to study the classroom teaching practices of teachers in Finland and the role of professional development of teachers in the use of instructional practices in the classroom using the data from the 2013 Teaching and Learning International Survey or most commonly referred to as TALIS. Literature Review Teachers’ Professional Development and Teachers’ Instructional Practices Classroom teaching practice is the main important factor in getting the positive learning outcome in the classroom. Many studies have described aspects of teaching practice which are related to effective classroom learning and student outcomes (Brophy and Good, 1986; Wang, Haertel and Walberg, 1993, cited in TALIS, 2013). In addition, numerous studies found that there were relationship between teachers’ classroom performance and student learning outcomes. Getting high level and consistent performance from teachers in the classroom is central to improving delivery of education service. The quality of education depends on the ability, hard work and dedication of the teacher. If a teacher fails to keep himself in touch with the rapid scientific and educational developments then he would become inefficient and ineffective. There are factors for shaping the quality of teaching. Among them, teacher training and professional development program are the main factor affecting the teachers’ practices. Training and development can be thought of as processes designed to enhance the professional knowledge, skills, and attitudes of educators so that they might, in turn, improve the learning of students. Training is an important part of teacher preparation programs, especially for those aspects of teaching that are more skill-like in their conception, but there are many other important aspects of teaching that can only be nurtured through reflective strategies and experiences (Rahman, et al, 2011). Training teachers is more likely to lead to diversity in practice at all levels of instruction. According to Asu (2004, cited in Rahman, et al, 2011) there are several outcome areas that are potentially affected by teacher training program. These include: (i) teacher knowledge, (ii) teacher attitudes and beliefs, (iii) teaching practice, (iv) school-level practice, and (v) student achievement. Ongoing professional development is also important factors in the teachers’ quality of teaching. According to Solheim, (2017), effective teacher learning and professional is important for student achievement. Teacher learning is a continuous process that promotes teachers’ teaching skills, master new knowledge, develop new proficiency which in turn, help improve students’ learning. Teachers with effective training and continuous professional training could become successful in their school. There are several programs for teachers’ professional development such as induction program and mentoring programs. They are the activities of the professional learning community practice. Professional learning community practice (PLC) is a very productive factor in developing the teachers’ professional backgrounds. Mentoring and coaching from colleagues is critical to the successful development of a new teacher. Great induction programs create opportunities for novice teachers to learn best practices and analyze and reflect on their teaching. If the teachers attended in induction and mentoring programs, they would implement their teaching practices effectively in the classroom. According to the Zey (1984, cited in Ingersoll & Strong, 2011), if the teachers have received effective training and induction program, they can implement their teaching profession effectively and keep their retention in their profession and then can provide the improved students’ learning. Figure 1: Zey’s Theory of Teacher Development (1984) Typical of theory underlying induction is Zey’s (1984) Mutual Benefits model, drawn from social exchange theory. This model is based on the premise that individuals enter into and remain part of relationships in order to meet certain needs, for as long as the parties continue to benefit. Zey extended this model by adding that the organization as a whole (in this case the school) that contains the mentor and mentee also benefits from the interaction. Moreover, teacher induction can refer to a variety of different types of activities for new teachers- orientation sessions, faculty collaborative periods, meetings with supervisors, developmental workshops, extra classroom assistance, reduced workloads, and, especially, mentoring. Mentoring is the personal guidance provided, usually by seasoned veterans, to beginning teachers in schools. In recent decades, teacher mentoring programs have become a dominant form of teacher induction (Fideler & Haselkorn, 1999; Strong, 2009; Britton, Paine, Raizen, & Pimm, 2003; Hobson Ashby, Malderez, & Tomlinson, 2009, cited in Ingersoll, & Strong, 2011) indeed; the two terms are often used interchangeably. According to the Zey’s teacher development theory, it can be concluded that there is an impact of the teacher’s preparation and induction on the teachers’ practice and students’ achievement. High-quality professional development, particularly in the form of mentoring or induction, may be key to increasing the likelihood that teachers will remain in the profession (TALIS, 2013). Although many studies argue for the importance of mentoring, evidence on the direct impact of mentoring is limited and inconclusive. A few studies suggest that mentoring appears to affect teachers‟ classroom management skills, as well as their ability to manage their time and workloads (Evertson & Smithey, 2000, cited in TALIS, 2013). In addition, many researches show that the influence teachers experience on their professional development strongly depends on the characteristics of the induction program, indicating that induction programs can contribute greatly to beginning teachers’ professional development, but often fail to do so because the programs lack essential characteristics. Various elements of induction programs appeared to be important, some of which have been implemented successfully in most induction programs. Important points of improvement are the organization of the induction program and the types of facilities that are offered; the capacity of mentors to challenge beginning teachers in their professional development; and the degree to which attention is paid to topics related to professional development, mainly pedagogy (Kessels, et al, 2010). The impact of professional development on classroom practices appears varied, with evidence to suggest that professional development may not directly support teachers with developing important instructional skills (Snow-Renner & Lauer, 2005; Desimone et al, 2002, cited in TALIS, (2013). According to Hattie (2009, cited in TALIS, 2013), teacher professional development appears to have the strongest impact on changes in teacher learning, followed by changes in actual teacher behavior, while less of an impact was found on student learning. And teacher professional development also has a positive association with teachers‟ self-reported increases in knowledge and skills and changes in classroom practices are: collaboration and active learning; continuity across time and activities; and differentiation (Garet el al, 2001, cited in TALIS, 2013). Based on the above literature review, the impact of the teachers’ professional development on the teachers’ instructional practices will be proved with the quantitative evident. Methodology Research Objectives 1. To study the use of instructional practices of the lower secondary school teacher in Finland. 2. To study the impact of teachers’ professional development on their use of instructional practice in the classroom. Hypotheses
In this paper, the data set (BTGFINT2) was used. “B”: lower secondary education (ISCED level 2); “T”: teacher-level data file. “G” is used for general questionnaire data. “FIN”: Finland and “T2” is used for the second round of TALIS conducted in 2013 In this data set the lower secondary education (ISCED level 2) Finland teachers were included. Total number of teachers is 2379 (Female=1961, Male 778). Source of Data In this paper, the TALIS 2013 questionnaire adapted from OECD was used. In this questionnaire, to know the professional development of teachers, the following background information is used.
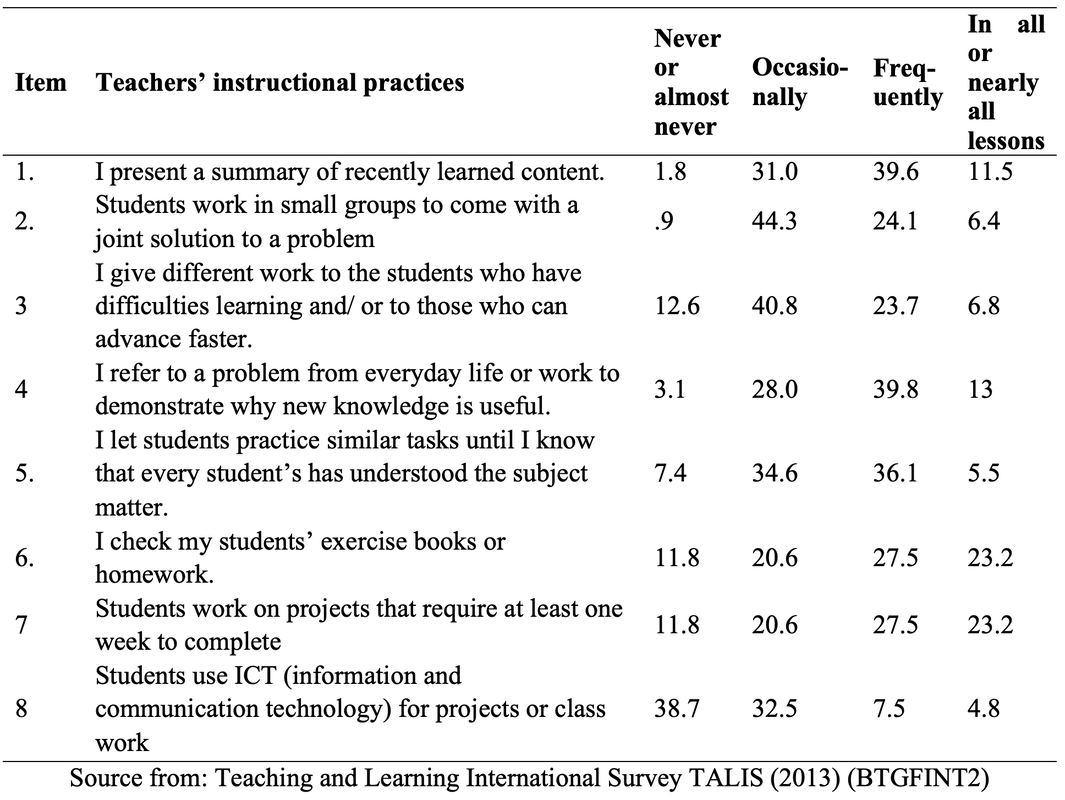
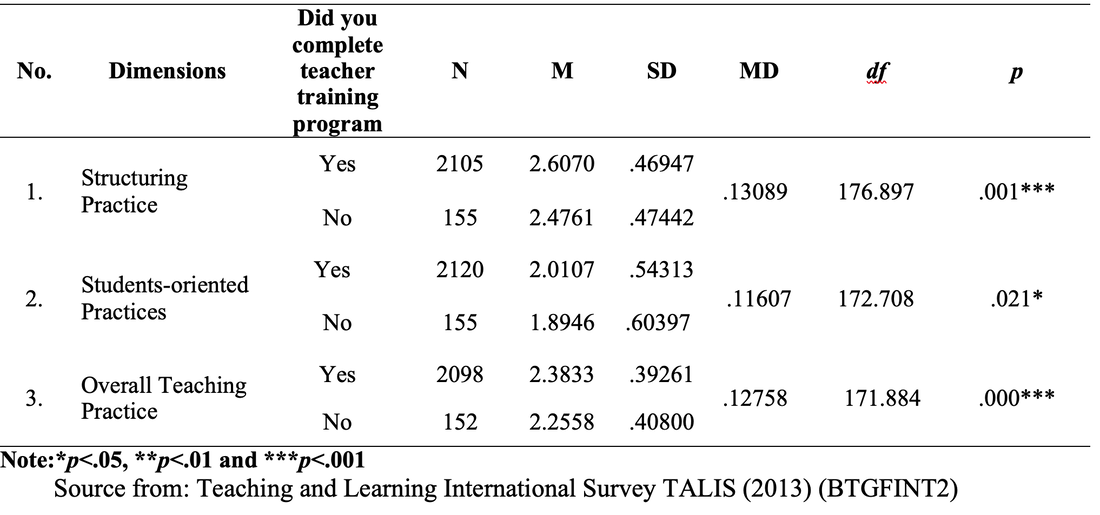
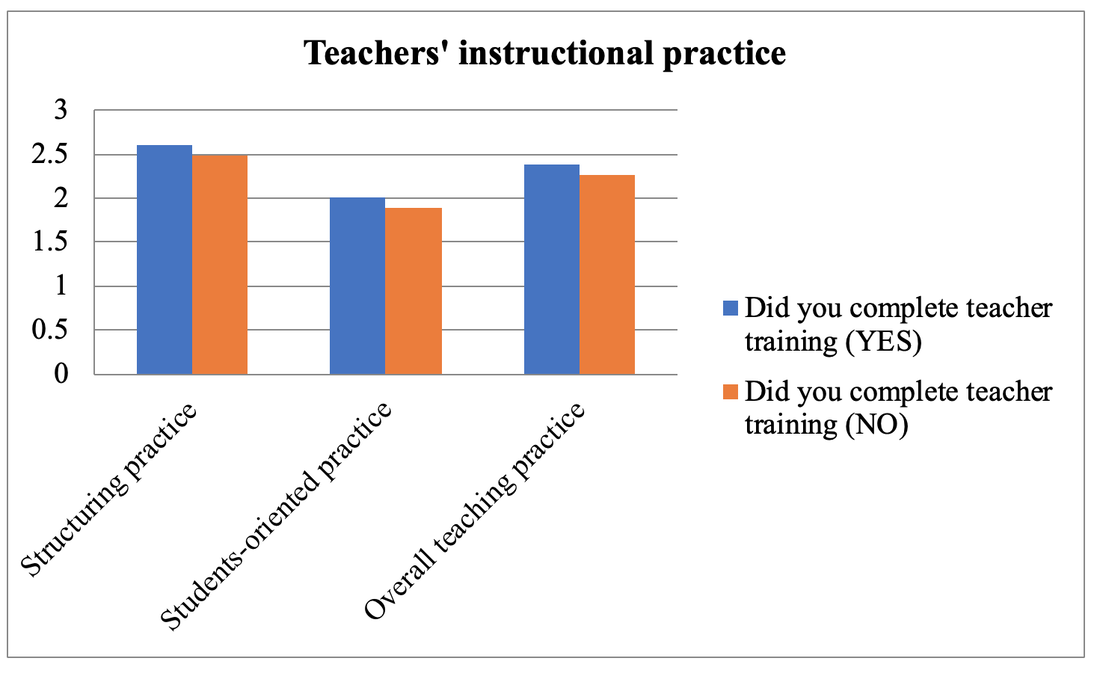
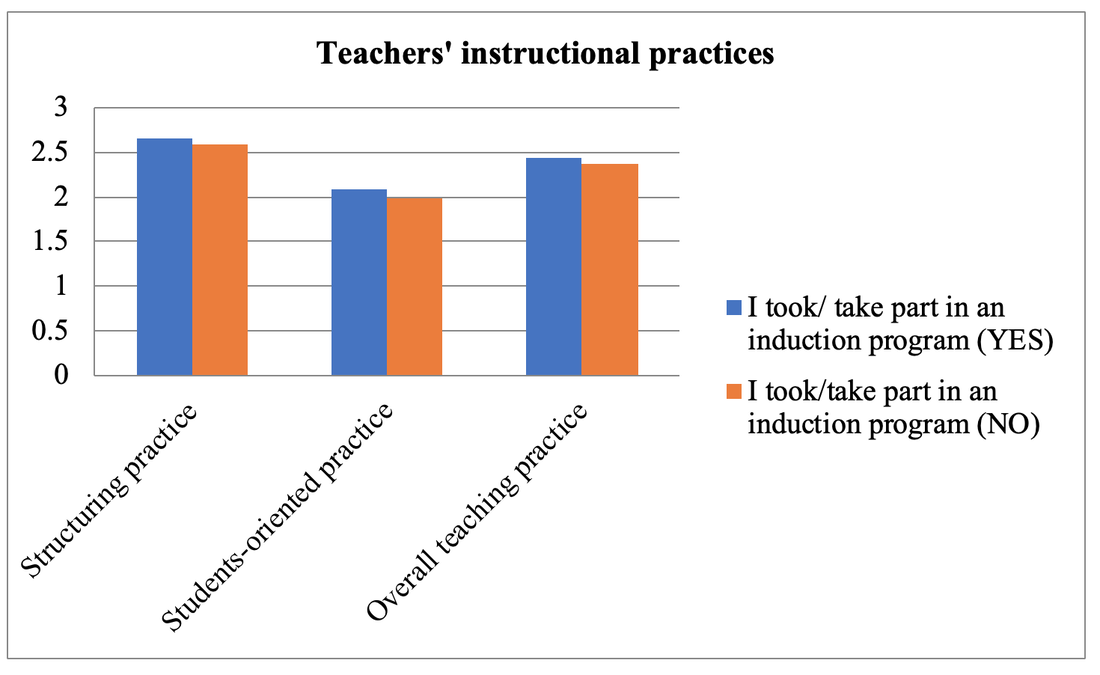
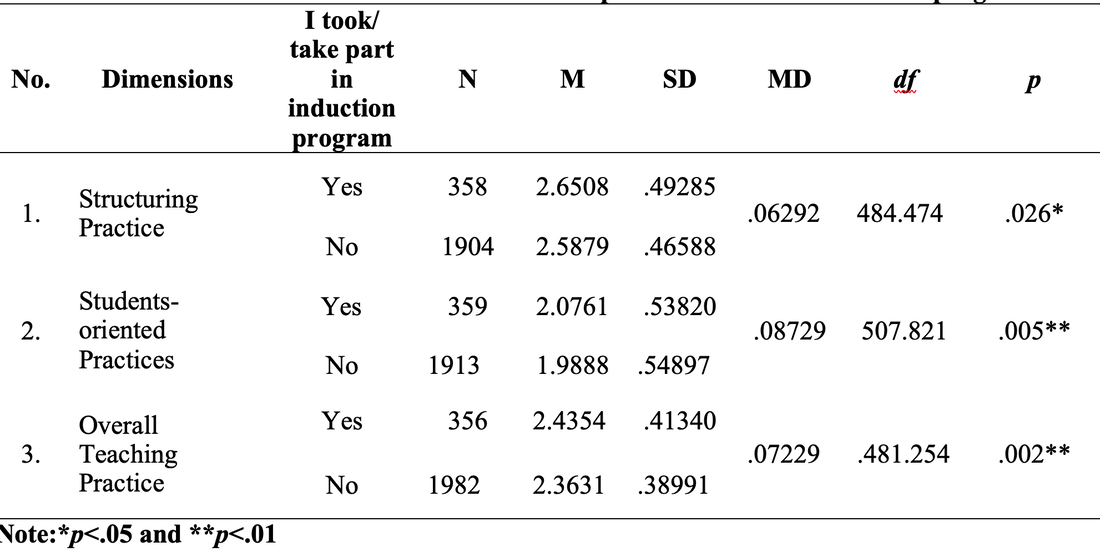
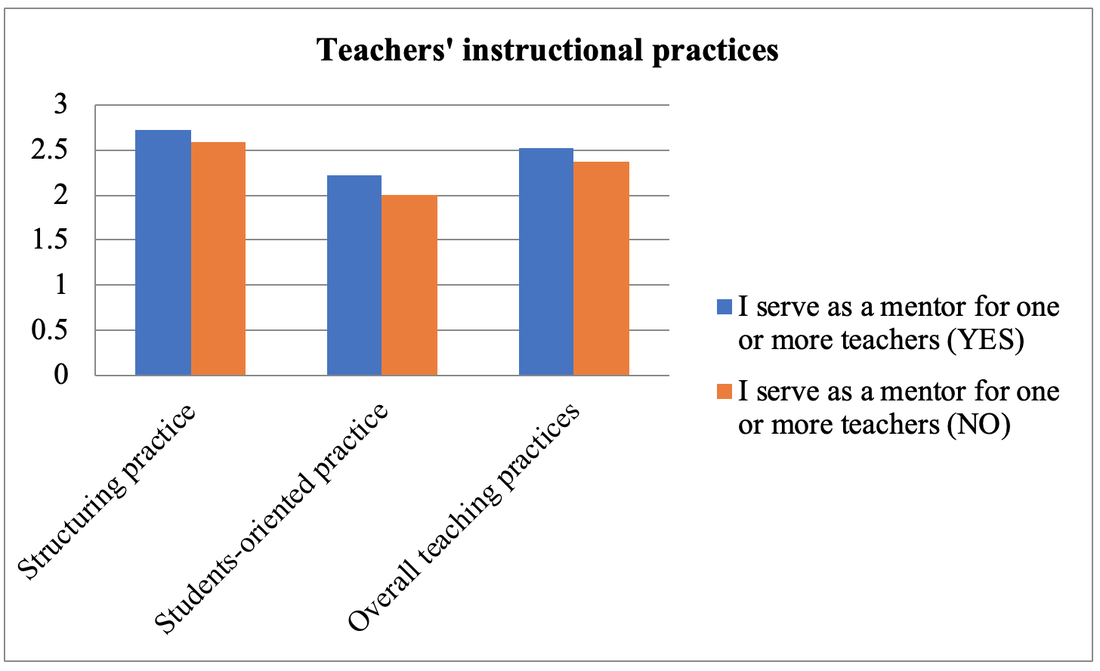
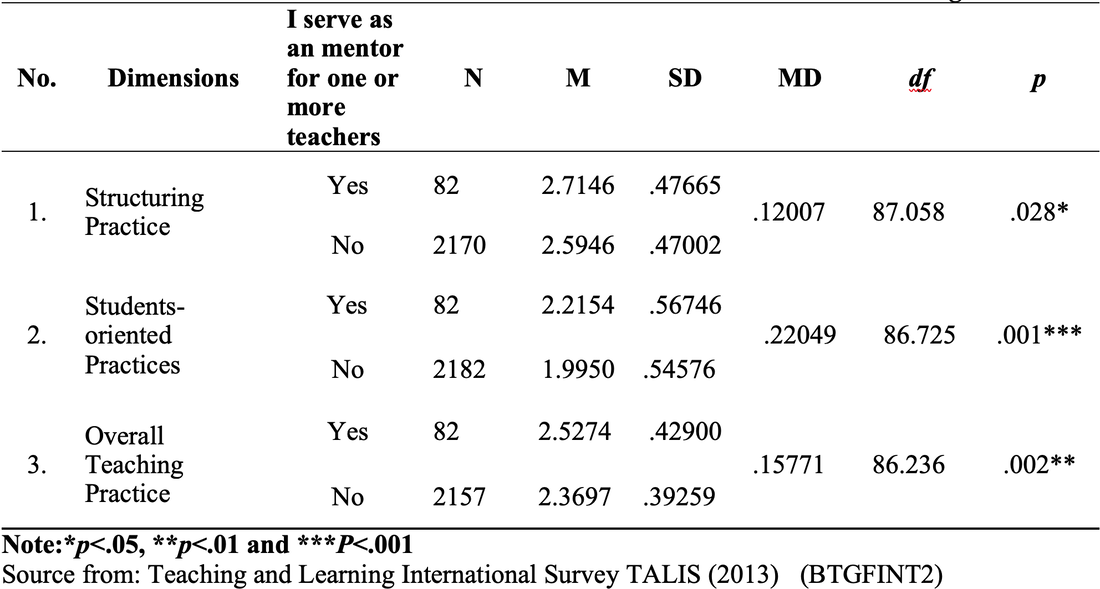
Method of Analysis To analyze the quantitative data, the Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version (20) was used. The data was analyzed by using descriptive statistics (percentage) for each question. In addition to this, t-test was used to compare the teachers’ practice in the classroom according to their professional development. Results and Findings The first section shows the use of instructional practices of the lower secondary school teachers in Finland and the second is the impact of teachers’ professional development on the use of teachers’ instructional practices. Findings for Use of Instructional Practices of the Lower Secondary School Teachers Table 1: Respondent Rate of Teachers on the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practices Table 1 shows the descriptive result of the use of instructional practices of the lower secondary school teachers in Finland. According to the result, most of the lower secondary school teachers present the summary of recently learned content to get engagement of students to new lesson. And they also use small group work to get students’ participation in their teaching learning process because they answer that 44.3% and 24.2% of lower secondary school teachers use small group work occasionally and frequently. In item three, most of the teachers use the teaching practice which gives different work to the students who have difficulties learning and/ or to those who can advance faster. Therefore, it can be concluded that most of the lower secondary school teachers can use the differentiated instruction according to the difference level of students. In item four, 28% and 39.8% of teachers use this practice occasionally and frequently. As this result, they can teach their subject by connecting everyday life experiences. This is the very useful teaching practice in the constructivist learning classroom. In item five, 34.6% and 36.1% of teachers give the students practice tasks until they know that every student’s has understood the subject matter occasionally and frequently. It can be concluded that they do drill and practice to get content mastery. In item six, according to the result, some teachers never check their students’ homework and some teachers check occasionally and frequently but 23.2 % of teachers check in all or most of the lessons. In item seven, 20.6% and 27.5% of teachers use projects that require at least one week to complete occasionally and frequently. But 23.2% of teachers use this teaching practice in all or most of the lesson. Item eight examines the use of ICT in the classroom. According to the result, 38.7% of teachers don’t use ICT for the project work. 32.5% of teachers occasionally use ICT and 7.5 % of teachers frequently use ICT in the classroom. But 4.8% of the teachers use ICT in all or almost of the lesson. The Impact of Teacher s’ Professional Development on the Teachers’ Instructional Practices Findings for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practice in Terms of Teacher Training As a result, the mean score of teachers who completed the teacher training was greater than that of teachers who didn’t complete the teacher training in all dimensions. Moreover, to be more specific, the independent sample t test was used to examine whether the difference for the use of teachers’ instructional practices in the classroom by the teacher training are significant or not. So the mean, standard deviation and the independent sample t test are described in Table 2. Table 2: t-Value for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practice in Term of Teacher Training. Figure 2. The Comparison of Mean Scores for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practices in term of Teacher Training Figure 2 showed that the mean score of teachers who completed teacher training was greater than that of teachers who did not complete teacher training in all dimensions, structuring practices, students-oriented practices, and overall teaching practices. After that, the independent sample t test was conducted to know the difference between the teachers with training and teachers without training and the result of t test as given in Table 2. As shown in Table 2, there is a significant difference in all the teachers’ use of instructional practices in term of teacher training at the p=001, p>.05 and p>001 level respectively. According to the result, it can be concluded that the teachers who completed teacher training can implement more instructional practices in the classroom than those who did not complete teacher training. Therefore, we can conclude that teacher training as the professional development of teacher has the impact on the use of teacher’s instructional practices. And the result is line with the theory of Zey’s teacher development model which means that there is a correlation between teachers’ professional development and the teachers’ classroom performances. Findings for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practice in Terms of Induction Program In order to find out the differences in the use of teachers’ instructional practice in the classroom among the teachers who took part in induction program and the teachers who didn’t take part in induction program, mean comparison was conducted. The independent sample t test was used in order to study whether the significant differences exist between the teachers who took part in induction program and the teachers who didn’t take part in induction program in the use of instructional practices. Figure 3. The Comparison of Mean Scores for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practices in term of Induction Program Figure 3 showed that the mean score of teachers who took part in induction program was greater than that of teachers without induction program in the use of teachers’ instructional practices. And then, the independent simple t test was conducted to examine the difference between those teachers. The result was shown in table 3. Table 3. t-Value for the use of teachers’ instructional practice in term of induction program Table 3 showed that the teachers with induction program were significantly different from the teachers without induction program on the use of instructional practices, at p>.05, p>.01 and p>.01 level respectively. This result is also in line with the Zey’s teacher development theory because this theory revealed that there was a correlation between the teachers’ induction and teachers’ classroom performance. As we can see in result of the Table3, we can concluded that the teachers who get the induction program can implement more their teaching learning process effectively than the teachers without induction program. Induction program is one of the important programs for the beginning teachers. Findings for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practice in Terms of Mentoring Activities Mentoring is also one of the important factors in the teachers’ professional development. Therefore, in order to know the impact of mentoring on the use of teachers’ instructional practices in the classroom, independent sample t test was used to find out the differences between the mentor and non-mentor. Mean difference between mentor and non-mentor teachers can be seen in the figure 4. Figure 4. The Comparison of Mean Scores for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practices in term of a Mentor Figure 4 indicated that the mean score for use of teachers’ instructional practices of mentor was greater than that of non-mentor teachers in teachers’ instructional practices. After that, the independent sample t test was conducted and the result of t test was given below. Table 4. t-Value for the Use of Teachers’ Instructional Practice in term of Mentoring According to the result, there were significantly differences between mentor and non-mentor in all dimensions (p>.05, p=001 and p>01 respectively). It can be concluded that the teachers who took part in the mentoring activities can implement their teaching learning process more than the teachers who didn’t take part in the mentoring activities. Mentoring is the main factor for developing teachers’ professional development and can give valuable instructional practices for the teachers. This is one of the important programs for beginning teachers to improve the teachers’ classroom performance and teachers’ retention. Summary of the Findings In the research findings, it was found that the teachers who completed the teacher professional development (teacher training, teachers’ induction and mentoring) can implement more their instructional practices than the teachers who didn’t complete the teacher’ professional development. Therefore, we can conclude that the teachers’ professional development have the impact on the teachers’ instructional practices in the classroom. Based on these research findings, we can develop a model as follows. Figure 5. Teachers’ Professional Development and Teachers’ Instructional Practices
Conclusion The objectives of this paper are to study of the use of instructional practices of lower secondary school teachers in Finland and to study the impact of teachers’ professional development on the use of instructional practices. To answer the research questions, the descriptive statistics and inferential statistics (t test) were used. The first portion of findings showed the use of instructional practices of teachers by using percentage in each item. The second portion showed the impact of teachers’ professional development on the use of instructional practices in the classroom. According to the t test results, we can conclude that the teachers who completed teacher professional development can implement more effectively than those who didn’t complete the teacher professional development such as teacher training, teacher induction program and mentoring program. Therefore, teachers’ professional development is the very important factor for improving teacher’ classroom practices. If the teachers attended effective teacher education program, they would implement their teaching learning process effectively. The quality of education depends on the quality of teachers, and the quality of teacher depends on the quality of teacher education program. Therefore, teacher education program or teacher professional development program should be considered as the main factors for improving the quality of education in every country. References Ingersoll, R., & Strong, M. (2011). The Impact of Induction and Mentoring Programs for Beginning Teachers: A Critical Review of the Research. Retrieved from http://repository.upenn.edu/gse_pubs/127 Kessels, C., Beijaard, D., van Veen, K., & Verloop, N. (2010). Supporting beginning teachers’ professional development with an induction program: When does a program make a difference? Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO). Project no. 411-02-203. Rahman, F., Jumani, N. B., Akhter, Y., Chisthi, S. H., & Ajmal, M. (2011). Relationship between Training of Teachers and Effectiveness Teaching. International Journal of Business and Social Science. Vol. 2 No. 4; March 2011. Retrieved from www.ijbssnet.com Solheim, K. (2017). Importance of teacher learning for students’ achievement. Retrieved from http://laringsmiljosenteret.uis.no/programmes-and-project/classroom-interaction-for-enhanced-student-learning-ciesl/news/importance-of-teacher-learning-for-students-achievement-article121594-22147.html Teaching and Learning International Survey TALIS (2013). Conceptual Framework. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development.
17 Comments
Abby Edison
5/31/2019 04:25:43 am
An educator should enroll in a professional development course which not only has a positive influence on the career growth of the educator but also increases his ability to understand the factors which should be taken into consideration to improve the teaching ability. There are a lot of institutions which offers professional development courses and a person could enroll in a professional development course through an online platform. To know more about the benefits associated with the professional development course, visit
Reply
Romesa
9/30/2019 09:48:10 am
Can you plz send me your questionnire?
Reply
Qingmin Shi
10/23/2019 09:49:12 am
Hi Hnin,
Reply
Habib ullah
4/25/2023 09:51:39 am
please share the article/thesis along with the questionnaire as I m also working on the same/similar like that. profound Regards
Reply
Oparinde Oluremi
2/5/2021 02:31:35 am
Very resourceful work
Reply
plz send me ur article as i am also working on professional development of teacher educators
2/5/2021 03:33:01 am
nice article
Reply
khadija
3/8/2021 03:42:20 am
Can you please send me your article and questionnaire?
Reply
8/23/2021 03:13:39 am
kindly send me your article and questionnaire as i am working on professional development and instructional practice of teachers.
Reply
Habib ullah
4/25/2023 09:50:03 am
please share the article/thesis along with the questionnaire as I m also working on the same/similar like that. waiting for your positive response, please
Reply
LOIDA CASTRO
8/30/2021 12:08:31 am
Wow! Nice Article.Kindly send me your article and questionnaire as i am working on professional development and instructional practice of teachers. Thank you. GOD BLESS
Reply
Habib ullah
4/25/2023 09:53:19 am
please share the article/thesis along with the questionnaire as I m also working on the same/similar like that. looking forward for your positive response , please
Reply
LIZA C. CUEVAS
10/2/2021 12:24:11 am
Nice research study... Kindly send me your article as I am working on professional development of teacher and their instructional practices.Thank you in advance. God bless!
Reply
CHUA SI MIN
11/12/2021 12:18:57 am
hi, would u mind send me your questionnaire as i am also working on effectiveness of professional development activities in Malaysia, your help is appreciated, thank you!
Reply
Tanveer Ahmad
1/2/2022 02:12:35 am
Can you please send me your article and questionnaire? I am also working on the teacher professional development. Thanks
Reply
nailla
1/10/2022 11:17:52 pm
Can you please send me your article and questionnaire? I am also working on the teacher professional development. Thanks
Reply
Habib ullah
4/25/2023 09:47:13 am
Great work
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
AuthorHnin Yu Soe ArchivesCategoriesFinland Image Attribution: M. Passinen [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html), CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/) or CC BY-SA 2.5 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5)], via Wikimedia Commons |
- Home
- About WVN
-
WVN Issues
- Vol. 1 No. 1 (Oct. 2017) >
- Vol. 2 No. 1 (Feb. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 2 (Jun. 2018) >
- Vol. 2 No. 3 (Oct. 2018) >
- Vol. 3 No. 1 (Feb. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 2 (Jun. 2019) >
- Vol. 3 No. 3 (Oct. 2019) >
- Vol. 4 No. 1 (Feb. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 2 (Jun. 2020) >
- Vol. 4 No. 3 (Oct. 2020) >
- Vol. 5 No. 1 (Feb. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 2 (Jun. 2021) >
- Vol. 5 No. 3 (Oct. 2021) >
- Vol. 6 No. 1 (Feb. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 2 (Jun. 2022) >
- Vol. 6 No. 3 (Oct. 2022) >
- Vol. 7 No. 1 (Feb. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 2 (Jun. 2023) >
- Vol. 7 No. 3 (Oct. 2023) >
- Vol. 8 No. 1 (Feb. 2024) >
-
Events
- CIES 2023, Feb. 14-22, Washington D.C., USA
- ICES 4th National Conference, Tel Aviv University, Israel, 20 June 2021
- 2022 Virtual Conference of CESHK, 18-19 March 2022
- ISCEST Nigeria 7th Annual International Conference, 30 Nov.-3 Dec. 2020
- 3rd WCCES Symposium (Virtually through Zoom) 25-27 Nov. 2020
- CESA 12th Biennial Conference, Kathmandu, Nepal, 26-28 Sept. 2020
- CESI 10th International Conference, New Delhi, India, 9-11 Dec. 2019
- SOMEC Forum, Mexico City, 13 Nov. 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Geneva, 14-15 Jan. 2019
- 54th EC Meeting, Geneva, Switzerland, 14 Jan. 2019
- XVII World Congress of Comparative Education Societies, Cancún, Mexico, 20-24 May 2019
- ISCEST Nigeria 5th Annual Conference, 3-6 Dec. 2018
- CESI 9th International Conference, Vadodara, India, 14-16 Dec. 2018
- ICES 3rd National Conference, Ben-Gurion University, Israel, 17 Jan. 2019
- WCCES Retreat & EC Meeting, Johannesburg, 20-21 June 2018
- WCCES Symposium, Johannesburg, 21-22 June 2018
- 5th IOCES International Conference, 21-22 June 2018
- International Research Symposium, Sonepat, India, 11-12 Dec. 2017
- WCCES Info Session & Launch of Online Course on Practicing Nonviolence at CIES, 29 March 2018
- WCCES Leadership Meeting at CIES, 28 March 2018
- 52nd EC Meeting of WCCES, France, 10-11 Oct. 2017
- UIA Round Table Asia Pacific, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 21-22 Sept. 2017
- Online Courses

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
